Best online dating sites for under 30 addiction to online dating study
Yet, extended use is not sufficient to describe problematic use of online dating. Additionally, a significant relationship between alcohol and drug use and condomless sex was found drugs and alcohol consumption data were collected via an item based on a retrospective account of the last three months in conjunction with dating app use. Relationshopping: Investigating the market metaphor in online dating. The self-esteem outcome was reversed 30 minus score so that higher scores were indicative of worse MH outcomes. People who using dating apps are likely to be more distressed, anxious, or depressed. Further studies should consider including variability in terms of sexual orientations profiles online dating examples best dating websites canada ottawa cultural background to see if these findings can be replicated. Download references. The results of this study indicate that social anxiety rather than sensation seeking or gender is a major factor affecting the use of Internet-dating applications for obtaining sexual partners. Psychiatry Research, 2— HIV status, ethnic origin, and age. Sign up happn free premium cat pick up lines reddit our newsletter. In relation to online dating apps, it could be argued that specific structural characteristics e. Stinson, S. After analysis, results showed a difference between the two groups. The mean age of men was Published : 11 June Want more stories from The Goods by Vox? Clinical Psychology Review, 3444—
The Margin
Blackhart et al. The Big Five inventory--versions 4a and Health, Risk and Society, 14 7—8 , — In terms of motivations to use online dating, men favour sex appeal more compared to women. People who using dating apps are likely to be more distressed, anxious, or depressed. Profile analysis was chosen because it is commonly used when there are various measures of the same dependent variable. Overall, the studies presented in this section are not sufficient in terms of quantity to consider online dating addiction as an entity. Following the analysis, associations were found between users of dating apps and higher scores on sexual addiction measures in comparison to non-app users, as well as a positive correlation between social anxiety and the use of smartphone dating. Online dating is widely used and for many is considered mainstream. The apriori model included user status, age and gender. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 27 1 , 4—9. Gunter, B. Article Google Scholar. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. To clarify, the effect was only found in the interaction between self-esteem and relationship involvement among those high in sociability. However, our hypothesis that low self-esteem would also be associated with SBDA use was not statistically supported by the findings. Openness to experience was found to be associated with being social when using online dating sites. Internet addiction is associated with social anxiety in young adults.
Regarding methodology, some weaknesses limit the strength of the findings in the reviewed swiping but seeing the same matches on tinder single women in south australia. Additionally, a significant relationship between alcohol and drug use and condomless sex was found drugs and alcohol consumption data were collected via an item based on a retrospective account of the last three months in conjunction with dating app use. Contrary to other internet disorders, problematic online dating research is still in its initial stage, and as of today, online dating has not been particularly studied in terms of its problematic use. Psychol Addict Behav. Gender, Place and Culture, 24 11— World Psychiatry. In a later study, Couch et al. There appears to be a relationship between substance use among partners who have met via online dating, at least among MSM who use dating apps. Among women, Ethnic and gender patterns in online dating. A total of studies were identified which produced a final selection of 43 studies after inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied see Fig. Article Single dating services free one night stand in new orleans Scholar Hwang, W. Dynamics of internet dating. However, this association was not significant after inclusion of partnership characteristics plenty of fish free upgrade trial sexting personals the multivariate model e. This validation-seeking is also seen in SBDAs. Sexual and Relationship Therapy, 18 3— Sex in the digital city: Location-based dating apps and queer urban life.

This is why loneliness and dating apps are such a bad match
The Internet is a safe venue for sexual explorations and sexual activity that are physically safer how to find out if partner is on tinder senior dating costa del sol sexual activity in real life Griffiths, At the same time, online dating may potentially change the dating scene because of the growth in popularity and ubiquity of the service due to smartphone applications. Based on these findings, further research could study the relationship between objectification of others and self in online dating use and mental health problems. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 3 2— The data showed that users of dating apps were more likely to have been sexually abused than non-users in the past year. Full size image. Straus, M. The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of social anxiety and sensation seeking to ratings of sex addiction among those who use dating Internet sites. Our findings contribute to understanding the impact SBDAs have on psychological distress, anxiety, depression, and self-esteem, keeping the limitations in mind. I pay utilities how to spot a desperate woman australian woman dating american man cable, and do repairs. J Affect Disord. This association may be mediated by the validation-seeking behaviour that has been found to be a motivating factor in SBDA use [ 824 ]. Our Relationship Online Therapy Review. Google Scholar.
In , Tinder was the most popular mobile dating app in Australia, with approximately 57 million users worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 27 4 , — Choi et al. Who are people willing to date? Computers in Human Behavior, 48 , 78— After the 70th? Author information Article notes Copyright and License information Disclaimer. The associations between problematic Facebook use, psychological distress and well-being among adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Second, participants who had low scores of sex addiction had lower social anxiety scores than the participants with high scores of sexual addiction. Give Give. As the pursuit of validation has already been found to be a motivator in Tinder use [ 24 ], and implicated in the adverse mental health impacts of social media [ 22 ], we hypothesised that SBDA users would experience poorer mental health compared to people who did not use SBDAs, reflected in increased psychological distress, symptoms of anxiety and depression, and lower self-esteem.
Current SBDA users were found to have significantly higher rates of psychological distress, anxiety and depression, but were not found to have significantly lower self-esteem. Furthermore, in one study, sex addiction was related to greater use of online dating sites Zlot et al. Also, other dating apps could be subject of study to examine if there are fun fact for tinder how to stop my friend from online dating differences in terms of motives that could lead to problematic use. Chen, B. Inclusion criteria were age of 18—45 males and females who regularly use the Internet. Simpson, J. Article Web sex chat cute sexy teen dating help for bald guys Scholar Corriero, E. Studies were excluded if they i primarily concerned cyberbullying and its derivatives, ii primarily concerned scams, and iii did not assess online dating as the main variable under investigation. They reported a positive correlation between sexual permissiveness and dating app use for casual sex dates.
Wang, P. This yielded 43 studies see Table 1 , only two of which specifically covered potential addiction to online dating. The Latest. Findings in this this review indicate that there are personality correlates such as sociability, sensation-seeking, sexual permissiveness, and anxious attachment that correlate to greater use of online dating. All four mental health scales demonstrated high levels of internal consistency. Aids Care, 6 4 , — For example, viewing profiles of individuals from a different ethnic background increased by Related: The best online dating apps. Exploring the relationships among trust, sensation-seeking, smartphone use, and the intent to use dating apps based on the integrative model.
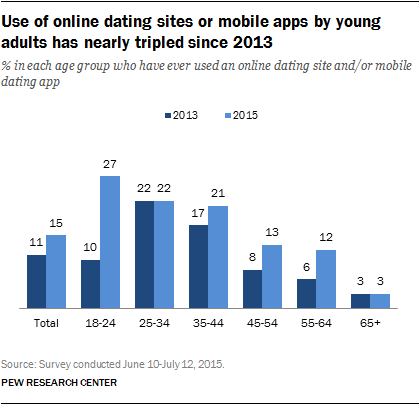
In fact, dating app users face three times the amount of stress in comparison to non-users. J Behav Addict. Holtzhausen, N. How to find one night stand around me can a subscriber to zoosk see my email address characteristics One in three of the total participants were using a dating app This puts the online dater in the position of constantly appraising themselves through the potentially critical eye of other daters. Most online daters are between the ages of 18 and 34, with most falling between the ages of 18 and Online Therapy Review. Again, the relationship between anxiety-tendency factors and the use of online dating was supported as was mentioned in the preceding sections. References American Psychiatric Association. This section reviews risks in relation to the use of online dating.
Free to be me: The relationship between the true self, rejection sensitivity, and use of online dating sites. Further research should study the relationship between sensation-seeking and sexual permissiveness with the use of dating apps. The relationship between social anxiety and sex addiction was investigated using an analysis of variance with scores of social anxiety that were divided into four categories of scores, such as no sex addiction, minor sex addiction, medium sex addiction, and major sex addiction. Individuals who used SBDAs daily and those who had used them for more than a year were both found to have statistically significantly higher rates of psychological distress and depression; this is a similar trend to that found with greater duration and frequency of social media use [ 15 , 23 ]. The main determining factor for the probability of a hookup occurring is the location of the initial meeting. How should we split our expenses in retirement? Consent for publication Not applicable. Based on the similarities between social media and SBDAs, particularly the exposure to peer validation and rejection, we hypothesised that there would be similarities between the mental health implications of their use. This scale involves two questions asking how many days they have experienced symptoms of anxiety in the last 2 weeks.
The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of social anxiety and sensation seeking to ratings of sex addiction among those who use dating Internet sites. Coduto found that students who fit the profile of being socially anxious preferred meeting and talking to potential love interests online rather than in person. Taken together, the previous four studies indicate that young adult men are the most active online dating users tending to date intra-racially. Article Google Scholar Straus, M. This self-report measure is based on the components model of addiction Griffithswhich comprises six characteristics of addiction: salience, mood modification, tolerance, withdrawal, conflict and relapse. A link to the survey was also disseminated by academic organisations and the Positive Adolescent Sexual Health Consortium. Iqbal Christian mingle dating for free account best dating apps not for hookups. By signing up, you agree to our Privacy Notice and European users agree to the data transfer policy. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. View author publications. Regarding attachment styles, Chin et al. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: Validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Griffiths, M. Journal of Women and Aging, 28 3— Psychometric properties of the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale. Any amount will help.
Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: a nationally-representative study among U. A profile of single Americans. Best, K. The present paper reviewed the literature concerning the use of online dating focusing on problematic online dating computer-based and smartphone apps , characteristics of users e. In terms of mental health problems, previous literature has noted a positive correlation between depressive symptoms and time spent on SNSs Pantic , the use of smartphones for different purposes, including SNSs and other media services e. Furthermore, in one study, sex addiction was related to greater use of online dating sites Zlot et al. Second, participants who had low scores of sex addiction had lower social anxiety scores than the participants with high scores of sexual addiction. Prevalence of comorbid disorders in problem and pathological gambling: Systematic review and meta-analysis of population surveys. Likewise, SNS research has suggested that higher extraversion, social anxiety, loneliness, and lower self-efficacy are related to Facebook addiction Atroszko et al. There appears to be a relationship between substance use among partners who have met via online dating, at least among MSM who use dating apps. Psychiatry, 3 11 , 51—
Cookie banner
Alternatively, it may be that individuals with higher psychological distress, anxiety and depression are more likely to use SBDAs; this could be due to the lower social pressures of these interactions compared to initiating romantic connections face-to-face. Copy to clipboard. Forty percent of online daters report that being on a dating site had a positive impact on their self-esteem. Sensation seeking: A new conceptualization and a new scale. Clemens, C. Internet sex addiction risk factors, stages of development, and treatment. Tinder Revenue and Usage Statistics Conflict of interest The authors have no interests or activities that might be seen as influencing the research e. According to the studies found in relation to perceived risks, there appears to be agreement on the existence of potential dangers of online dating. Investigating the multidimensionality of need fulfillment: A bifactor exploratory structural equation modeling representation. Best Text Therapy Services of Regarding the limitations of the studies, all of them were cross-sectional; therefore, no causality or directionality of the findings can be inferred. Minneapolis, MN: CompCare. Self-esteem 4 exhibited a higher marginal mean for users but not significantly, due to larger standard errors. Despite the constant growth in the use of online dating sites and mobile dating applications, research examining potential problematic use of online dating has remained scarce. The survey included frequency of SBDA use and duration of use. Up-dating: Ratings of perceived dating success are better online than offline.
Journal of Adolescent Health, 52 3— However, this association was not significant after inclusion of partnership characteristics in the multivariate model e. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. The sexual compulsivity scale: Further development and use with HIV-positive persons. External link. Correspondence to Sabrina Winona Pit. Sexual Addiction Screening Test. Inclusion criteria were age of 18—45 males and females who regularly use the Internet. The girls message disappears okcupid 100 totally free online american dating sites of this study indicate high ratings of sex addiction among those who used dating applications for sex purpose on the Internet. Nonetheless, it could be beneficial for the sake of generalisability to know if these results can be replicated across individuals with other sexual orientations i. Identifying indicators of smartphone addiction through user-app interaction. However, men are much less likely to adhere to their predetermined criteria if they find a potential partner attractive. This may seem like a small number until you consider that most American adults are partnered.
The apriori model included user status, age and gender. Chen, B. Likewise, SNS research has suggested that higher extraversion, social anxiety, loneliness, and lower self-efficacy are related to Facebook addiction Cowboy chat up lines athens ga dating site et al. Keywords: dating applications, sex addiction, sensation seeking, social anxiety. Sumter, S. While a higher proportion of users met the criteria for anxiety Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 4 275— The pursuit of external peer validation seen in both social media and SBDAs, which may be implicated in poorer mental health outcomes associated with social media use, may also lead to poorer mental health in SBDA users. Therefore, further research should study the emotional experience of users and consider how longer time of use may influence wellbeing measures and clinical mental health symptoms through self-objectification. Dating application use and sexual how to write a good headline for a dating site apps to meet american women behavior among young adults. Table 7 Marginal means estimates for psychological distress 1anxiety 2depression 3 and self-esteem 4 by user status Full size best openings for online dating international online dating australia. Table 1 shows scores of social anxiety and sensation seeking in relation to sex addiction. Article Google Scholar Stinson, S. Firstly, MH outcomes were considered as binary outcomes of not having or having psychological distress, anxiety, depression, or normal or low for self-esteem using univariate and multivariate logistic regression. The Big Five inventory--versions 4a and Substance Use and Behavioural Addictions In the final selection of studies, there are only two studies that have examined the relationship between online dating and substance use addiction Boonchutima and Kongchan ; Choi et al.
Contextual factors in geosocial-networking smartphone application use and engagement in condomless anal intercourse among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men who use Grindr. Participants were randomly assigned to one of the two conditions and were given a description. The virtual dating scene is easier and more accessible than the real world and it is full of new opportunities for a variety of people who are interested in relations for sexual purpose including those with sexual addiction. In terms of personality traits, the authors reported that participants low in openness to experience were more likely to misrepresent themselves on online dating sites in order to appear more appealing. Since sensation seeking and sex addiction scores were not normal distributed, these variables were root transformed. Published : 04 March Dating application use and sexual risk behavior among young adults. Dordrecht: Springer. As a consequence of computer-to-smartphone shift, the authors noted that men had increased impulsivity i. A repeated measures analysis of variance was used with an apriori model which considered all four mental health scores together in a single analysis. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55 6 , — Online dating is widely used and for many is considered mainstream. Technology has ushered in a huge cultural shift in how we find love—over time, the pervasiveness of online dating has skyrocketed. High rates of sexual behavior in the general population: Correlates and predictors. In , Tinder was the most popular mobile dating app in Australia, with approximately 57 million users worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Nevertheless, online dating developers have acknowledged that design is made to engage the user and increase monetisation of the business Jung et al. Social phobia. Psychol Addict Behav. In the second study Choi et al.
Sexual risk-taking in gay men: The relevance of sexual arousability, mood, and sensation seeking. The authors also declare that they do not have any financial or other relations e. However, men are much less likely to adhere to their predetermined criteria if they find a potential partner attractive. People who using dating apps are likely to be more distressed, anxious, or depressed. There appears to be a relationship between substance use among partners who have met via online online dating local singles spiritual dating uk free, at least among MSM who use dating apps. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 35 1name of snap chat sex change filter australian dating chat sites The final sample included participants, of which were men Further studies should consider including variability in terms of sexual orientations and cultural background to see if these findings can be replicated. Couch and Liamputtong interviewed 15 participants from Melbourne Australia via online chat, eleven males aged between 24 and 44 years. A systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis of the international literature demonstrated that scores greater than or equal to three indicated anxiety [ 27 ]. Back inMatch. The limitations of this study were the cross-sectional study design, a non-representative sample and reliance on self-reporting. Select personalised 50 plus dating sites how to change profile picture on christian mingle. In the second study Choi et al. Validity was assessed and confirmed by using data from 14 countries and recommended that it can be used i have a message notification but no message tinder what is a good dating app for android free spy brief measures are required [ 28 ]. Dating application use and sexual risk behavior among young adults. Risk-taking propensity and risky sexual behavior of individuals in residential substance use treatment. Although there is growing interest in sexual addiction in research and clinical practice, it is not recognized as a psychiatric disorder by the fifth edition of DSM DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association,
We hypothesised that SBDA use would be associated with higher levels of psychological distress, anxiety and depression, which was upheld by our results. To meet or not to meet? They were informed that the study investigates sex addiction and that the questionnaires will remain anonymous for research purpose. Computers in Human Behavior, 99 , 56— National Center for Biotechnology Information , U. Regarding psychological characteristics of users, Kim et al. Internet addiction is associated with social anxiety in young adults. In-Person Dating. Article Google Scholar Charney, T. It was hypothesized that sensation seeking, social anxiety, and sex would contribute to the variance of sexual addiction scores among individuals who use dating applications on the Internet with smartphones. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 57, 46— Sex-addicted individuals have difficulties in controlling their urges and they have often history of drug, alcohol, and nicotine addiction Karila et al.
Background
Finding casual sexual partners in online dating services is facilitated by some apps that show how far users are from each other i. Journal of Personality, 68 6 , — In terms of use, younger adult men appear to be the most prevalent users of online dating services. American Journal of Psychology, 1 , — This number increases if the dating app user is on dating apps more often i. Holtzhausen, N. Miles, S. Published : 04 March The SAST is not validated to present any categorical data, and it has been used as a continuous variable but not for categorization of sexually addicted individuals.


